Is your organization regularly impacted by staff absences or employee turnover?
Have your business processes ever been put on hold because an employee who performs specific tasks was out sick or on vacation?
Are you looking to increase your employees' skill sets and engagement?
These are just a few of the reasons that many companies provide cross-training opportunities for their team members.
But what is this type of training and why is it so important?
What is cross-training?
| Cross-training, also known as cross-skilling or multi-skilling, involves training employees in various roles beyond the responsibilities or specific skills of their main role. |
There are numerous benefits of cross-training employees, from fostering organizational know-how to empowering your workers with additional skills. Like increased collaboration.
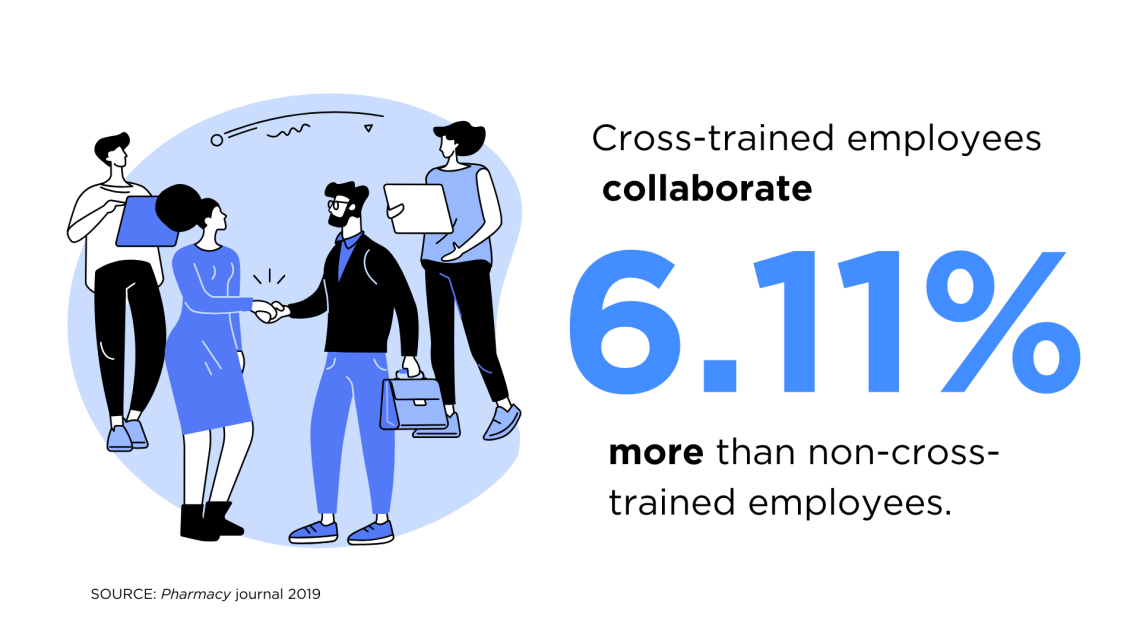
A study published in 2019 found that cross-trained employees collaborate 6.11% more than those that are not cross-trained. Another study published in 2025 shows that multi-skilling or cross-training can lead to cost-savings.
Why is employee cross-training important?
Aside from cost-savings, there’re many reasons companies like Toyota leverage cross-training.
With cross-training, employees can feel more competent, with greater adaptability, able to take on different tasks and fill in for colleagues, enabling a culture of continuous improvement.
Being able to fill in for colleagues is key because it means that operational disruptions are minimized, ensuring business continuity during absences, turnover, or peak workloads.
Cross-trained employees also translate to more knowledgeable employees, safekeeping institutional knowledge through knowledge sharing.
Cross-training benefits
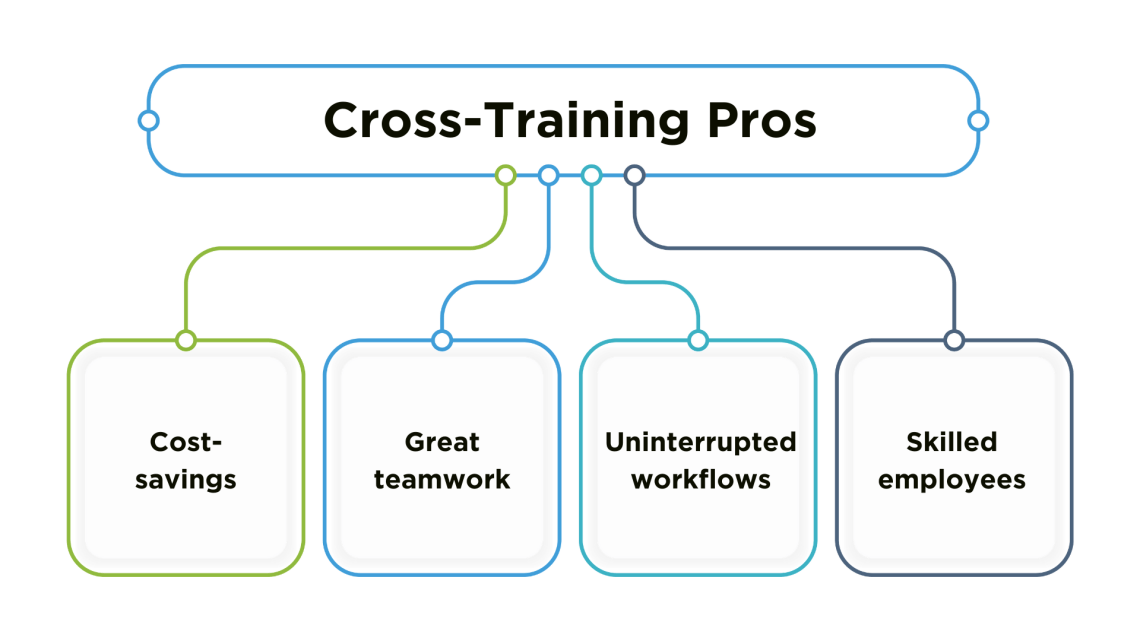
Cross-training increases collaboration
Does teamwork really make the dream work? According to a report from LinkedIn, the answer to that question is a resounding yes.
Collaboration is a vital tool for increasing productivity, employee engagement, and employee well-being. Employees who can collaborate with others tend to see themselves as part of a larger team. They are also empowered to view projects from different perspectives.
Cross-training often serves as a sort of "job rotation" for employees, which can increase engagement as they get to do something new and spend time with coworkers from different departments they don't normally interact with.
Learning platforms like Docebo can integrate seamlessly with several collaborative business apps, including Slack, Google Drive, and Microsoft Teams. This fosters easy communication between teams and the learning materials offered through your onboarding and cross-training program.
New hires and team members who are learning new roles can use these integrations to access a centralized area for training materials and information.
Cross-training saves money
Employees who are cross-trained to take on additional responsibilities beyond those specifically associated with their job title save the company money in several ways, including:
- Covering staffing shortages. These shortages can otherwise have negative impacts on the services provided to customers and other crucial aspects of the business.
- Increasing retention. Impact retention and reduce employee turnover through engagement and improved job satisfaction.
- Prioritizing quality control. Ensure standardization of services by having enough employees to perform specific tasks.
- Seizing opportunity. Discover hidden talents among team members as they learn different roles, and support staff in their professional development efforts.
As noted by Walden University, when companies can fill job positions internally, they generally see a positive impact on their financial bottom line by not having to engage in outside recruitment efforts.
They also see reductions in the money and time involved in onboarding. After all, the employee is already familiar with the company's mission, goals, policies, and procedures.
Cross-training covers gaps in staff
Vacation time, sick time, family leave, retirement... There are many reasons for gaps in staff and for staff to take on additional responsibilities to cover the absences of coworkers.
Have you ever gone to a place of business only to be told that the person who provides the services you need is out for the day or even the week?
The consequences of being short-staffed can have significant impacts on employees and customers alike. Customers are inconvenienced by being told to come back later.
Short staffing also leads to employee burnout. It can even create a lack of versatility that is needed for a business to thrive.
Succession planning (identifying important positions to fill in the organization) is also an important benefit of cross-training.
Cross-training employees grow their skills
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment in the field of training and development specialists is expected to grow by 6 percent by 2032.
That is faster than the average for all occupations. As reliance on technology increases, the training needs of employees to upskill or reskill is essential to their professional development.
Cross-training employees, whether merely shadowing team members from other departments or training to fill in at another position, acquire new skills in the process.
So, in essence, cross-training employees can help staff further their career goals, enabling professional growth and internal mobility, while reducing the need for outsourcing.
In many industries, professional development opportunities are required for workers to keep their certification or license. With an LMS platform like Docebo, professional development can be achieved in many different forms, such as:
- Microlearning tasks
- Gamification
- Instructor-led learning
- Learning content created by department leaders for the purpose of cross-training
Drawbacks of cross-training
While cross-training offers significant benefits like reducing turnover, increasing job satisfaction, and standardizing processes, it’s not without its challenges.
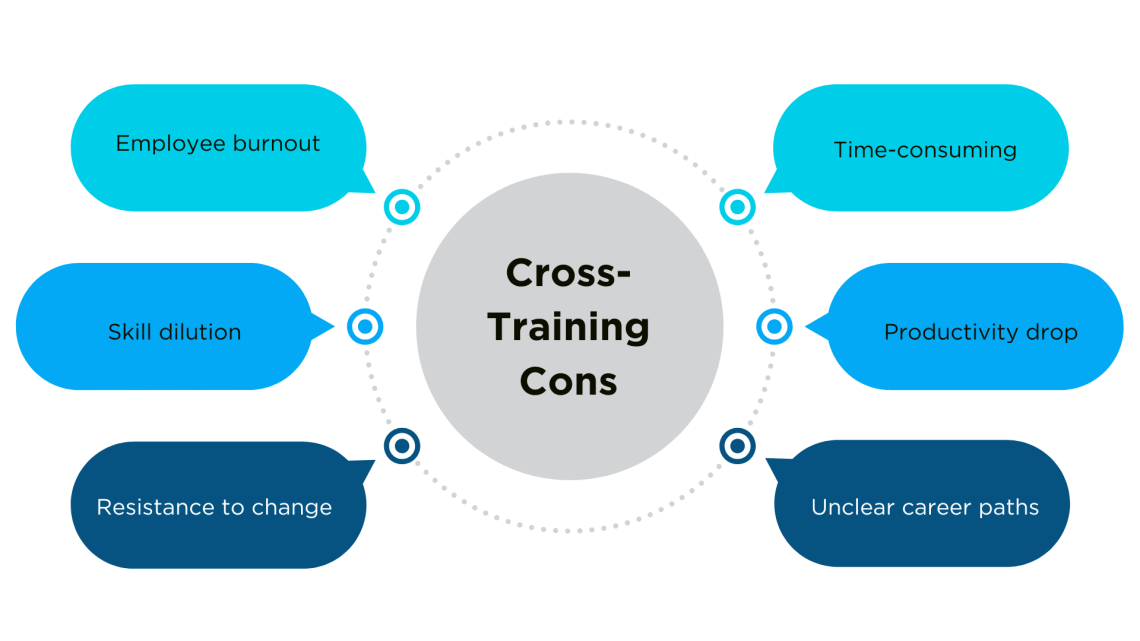
Poorly planned cross-training initiatives can lead to burnout, resistance, and inefficiencies if not managed properly. Here are some potential cross-training pitfalls organizations should consider:
- Employee Burnout & Increased Workload – Cross-training can overwhelm employees if they are expected to take on additional responsibilities without adjustments to their workload. It’s important to balance cross-training with clear expectations and adequate support.
- Skill Dilution & Lack of Mastery – While cross-training helps employees gain new skills, it may limit deep expertise in one area. If employees are frequently rotated, they may not have the time to master any one role, leading to decreased proficiency in critical tasks.
- Resistance to Change – Some employees may resist cross-training due to fear of increased responsibilities, job security concerns, or discomfort with change. Clear communication, incentives, and leadership support are essential to encourage participation.
- Time-Consuming & Resource-Intensive – Implementing cross-training requires structured learning programs, mentoring, and oversight, which can take time and divert resources from daily operations. Organizations need a well-planned training strategy to ensure it’s effective and doesn’t disrupt productivity.
- Temporary Drop in Efficiency – As employees learn new skills, there may be an initial dip in productivity. Mistakes and slower execution are expected while they get accustomed to new responsibilities, requiring patience and ongoing support.
- Unclear Career Pathways – If cross-training is not tied to clear career progression opportunities, employees may feel they are taking on extra work with no reward. Organizations should ensure that cross-training leads to promotions, upskilling, or leadership development to keep employees engaged.
Without careful planning, cross-training can cause an employee to feel overwhelmed. It can even result in employees becoming generalists who know a little about a lot of things but not enough to handle unique situations as they arise. When implementing your cross-training plan, here are some tips to remember.
Cross-training examples
Cross-training can take many forms depending on the industry and business needs. Here are real-world examples of how organizations successfully implement cross-training:
- Manufacturing & Production (Toyota's Lean Manufacturing)
Toyota uses cross-training as part of its lean manufacturing and Kaizen principles to ensure employees can perform multiple tasks on the assembly line.
- Customer Service & Support
A company trains customer service representatives in basic IT troubleshooting so they can handle common tech-related inquiries without escalating to another department.
- Retail & Hospitality
The food industry uses cross-training to enhance flexibility, efficiency, and service quality. For example, at Moe’s Original BBQ, there was a strict separation between front-of-house and kitchen staff, causing bottlenecks during peak times.
To address this, the restaurant cross-trained employees so that kitchen staff could help with tasks like answering phones, bagging to-go orders, and bringing food to tables. Likewise, front-of-house employees learned how to assist with basic prep work like filling sauce cups and restocking ingredients when the kitchen was overwhelmed.
This approach allowed the restaurant to adapt to fluctuating demand, improve customer service, and increase productivity—ultimately leading to higher catering sales and reduced employee turnover.
- Healthcare
Nurses in hospitals are trained in multiple specialties, such as pediatric care, emergency response, or surgical assistance.
- Technology & IT Teams
Software developers are cross-trained in DevOps practices so they can handle both development and deployment tasks.
- Sales & Marketing
A company cross-trains sales representatives in content marketing so they can write blog posts and create LinkedIn content that supports their sales strategy.
- Finance & HR
HR professionals are trained in basic financial analysis to better understand payroll, compensation structures, and budgeting.
How to develop an employee cross-training plan
A well-structured cross-training plan ensures that employees develop new skills, enhance flexibility, and improve operational efficiency without disrupting productivity. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating an effective cross-training program:
1. Identify Business Needs & Goals
- Determine why cross-training is necessary—whether it’s to improve service, reduce skill gaps, enhance employee engagement, or increase workforce agility.
- Identify key roles and tasks that could benefit from cross-training (e.g., frontline staff learning inventory management or customer service teams learning basic IT troubleshooting).
2. Assess Employee Skills & Interests
- Conduct skills assessments to determine which employees have transferable skills.
- Survey employees to gauge interest in learning new roles, ensuring cross-training aligns with their career growth.
3. Select Roles & Define Training Paths
- Choose which roles should be cross-trained while maintaining balance between specialization and flexibility.
- Establish structured learning paths that outline step-by-step training goals, including shadowing, mentorship, and hands-on practice.
4. Implement Training with a Mix of Methods
- Use job rotation to allow employees to gain real experience in different roles.
- Leverage an LMS or learning platform to provide structured e-learning modules, certifications, and skill tracking.
- Pair employees with mentors or experienced colleagues for hands-on guidance.
5. Monitor Progress & Provide Feedback
- Use tracking tools (like performance evaluations, checklists, and supervisor feedback) to measure learning progress.
- Set clear performance benchmarks so employees understand expectations.
- Provide regular feedback and support to reinforce learning and address challenges.
6. Recognize & Reward Cross-Training Success
- Offer incentives such as promotions, salary increases, or recognition programs to motivate employees.
- Clearly communicate how cross-training contributes to career development to increase engagement.
7. Continuously Evaluate & Improve
- Gather employee feedback to refine the program.
- Analyze business impact by measuring productivity, service improvements, and employee retention.
- Adjust training as business needs evolve to keep cross-training relevant and effective.
By strategically implementing cross-training, companies can build a more versatile, engaged, and resilient workforce, ensuring long-term business success.
Employee cross-training plan template
Creating an employee cross-training plan can start off very easily.
With just an Excel spreadsheet.
Here’s what you’ll want to cover:
1. Identify Employee Candidates for Cross-Training
The first step is to determine which employees are best suited for cross-training based on:
- Their current skills and experience
- Their interest in learning new roles
- Business needs and skill gaps within the organization
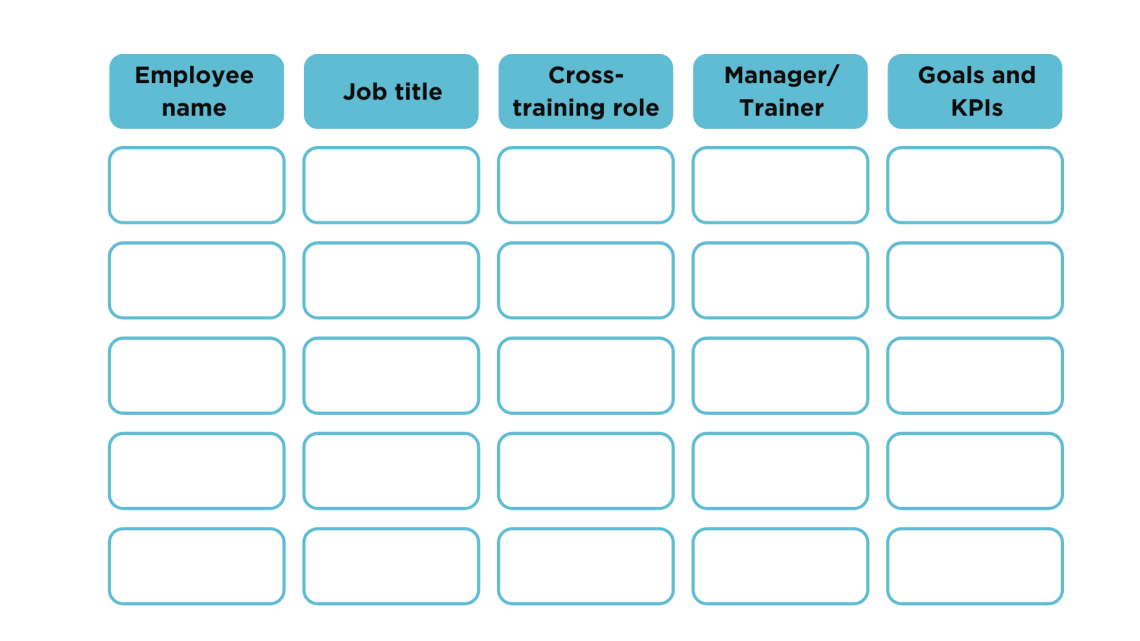
So the first few columns in that spreadsheet might include something like, “Name,” and “current job title.”
2. Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities
The next step is to ensure employees gain a comprehensive understanding of the new role. So clearly define:
- Key tasks and responsibilities within the position
- The skills required to perform effectively
- How the role contributes to the team and business goals
So the next column in the spreadsheet should be called “Role,” and it should break down the job into specific tasks to make training more manageable and allow progress tracking.
3. Designate Responsible Managers or Trainers
A successful cross-training program requires dedicated trainers or mentors who can provide hands-on guidance.
For this “Manager” or “Trainer” column, you will include the name of the person who will oversee the training process. You can also include additional tabs outlining their responsibilities.
4. Determine the Goals for Cross-Training
Cross-training should align with both employee development and business needs. In this column, you will list the goals for cross-training, which should be specific and measurable. These can allow you to define key performance indicators (KPIs), which you can include as another tab, and can involve the results from skill proficiency assessments, completion of training milestones, and manager and peer feedback.
By following this structured approach, organizations can create an effective and scalable cross-training program that improves workforce agility, career development, and operational efficiency.
Learn more about how effectively cross-train employees
Cross-training employees is an important aspect of career development for your team, as well as an important aspect of succession planning for your organization.
To learn more about how Docebo's platform can help with your company's cross-training efforts, book a demo.
